RVSKVV B.Sc Horticulture Science: Fees 2025, Course Duration, Dates, Eligibility
Course Description
Bachelor of Science Horticulture Top Colleges, Syllabus, Scope and Salary
B.Sc. in Horticulture is a 3 years full time under graduate course which is divided into 6 semesters. Horticulture is the branch of Agricultural Science that deals with the cultivation of vegetables, plants, flowers, herbs, fruits, shrubs, bushes, gardens, and landscaping for gardens, ornamental trees, maintaining nurseries, green houses, orchards and plantations and also floriculture or cultivation of flowers.
The branch of study now has direct and indirect applications in food technology industries as production, cultivation, harvesting and storing of vegetables have all become highly mechanized. These plants are grown under strictly controlled conditions using sophisticated sensors, and biological control of pests and diseases. It is of the utmost importance for all commercial as well as resource-limited farmers to plant deciduous fruit crops, some fruit crops and rootstocks that are adapted to their specific climatic and soil conditions.
The average annual course fee ranges anywhere between INR 5,000 to 2 lakhs depending upon the institute offering the course. The average salary offered for this course in India to successful postgraduates of the course ranges between INR 2 to 10 lakhs depending upon the candidate’s expertise in the field.
B.Sc. Horticulture: Course Highlights
Shown below are some of the major highlights of the course.
| Course Level | Under Graduate |
| Duration | 3 years |
| Examination Type | Semester System |
| Eligibility | 10+2 |
| Admission Process | Counselling after taking Entrance Examination |
| Course Fee | INR 5,000 to 2 lakhs |
| Average Starting Salary | INR 2 to 10 lakhs |
B.Sc. Horticulture Top Institutes
Some of the institutes or colleges offering the course in the country with the corresponding locations and fees charged by the respective colleges are listed below.
| COLLEGE NAME | CITY | AVERAGE ANNUAL FEE IN INR |
|---|---|---|
| Lovely professional university | Chandigarh | INR 4,76,000 |
| BFIT group of institutions | Dehradun | INR 2,12,000 |
| Lovely professional university | Jalandhar | INR 4,76,000 |
| Uttaranchal college of biomedical sciences and hospital | Dehradun | INR 2,53,000 |
| Sai institute of paramedical and allied sciences | Dehradun | INR 2,33,000 |
| Dev bhoomi institute of management studies | Dehradun | INR 2,60,000 |
| Dolphin PG institute of biomedical and natural sciences | Dehradun | INR 2,75,000 |
| Doon business school | Dehradun | INR 3,17,000 |
| Annamalai university | Chennai | INR 1,08,000 |
| Hemwati nandan bahuguna garhwal university | Uttarkhand | INR 5,050 |
| Banaras Hindu university | Varanasi | INR 1,000 |
| Andhra university | Visakhapatnam | INR 48,000 |
| Dibrugarh university | Dibrugarh | INR 52,360 |
Eligibility for B.Sc. Horticulture
Entry to this field starts from undergraduate level. After completion of 10+2 in Science stream (class 12th) with chemistry, physics, and maths/ biology/ agriculture as the subjects one can opt for Bachelor’s degree in Horticulture as a separate discipline or as a subject of BSc Agriculture Science.
B.Sc. in Horticulture: Admission Process
The candidates those desire to take admission in UG in Horticulture has to appear in HORTI CET Entrance Test conducted by itself have to qualify this exam by securing at least minimum qualifying marks to get the admission. The candidates will get the admission through a counselling a process just after the result announced.
B.Sc. in Horticulture: What is it all about?
B.Sc. Horticulture program is all about cultivation of plants, starting from seed related study to scientific study of cultivation, plant diseases, genetics of plants etc. It is all about the application of scientific knowledge in plant cultivation and thus increase productivity and yield. From achieving the said goal of improved productivity, this study makes use of concepts of Biochemistry, Biology, and Genetic Engineering etc.
The markets for deciduous fruit, from both locally and overseas, are becoming increasingly competitive, because of the marginal climatic conditions for the production of high quality deciduous fruit. Many local fruit producers are in search of alternative crops to reduce their risk. These crops include persimmons, olives, berry fruit, dates, figs, cactus pears and various nut crops. Many of these crops are more adaptable to marginal areas and require less water.
Some are suited to developing agriculture, if they do not require the same level of inputs as the main deciduous fruit crops and some require much labour, they presenting job creation opportunities for less skilled people.
B.Sc. in Horticulture: Syllabus and Course Description
A Semester - wise syllabus of the course is tabulated below.
| SEMESTER I | SEMESTER II |
|---|---|
| Introduction to soil science | Fundamentals of statistics |
| Crop physiology | Elements of computer application |
| Fundamentals of horticulture | Plant parasitic nematode |
| Plant propagation | Tropical and subtropical fruits |
| Fundamentals of extension education | Fundamentals of food technology |
| Growth development of horticulture crops | Principles of genetics |
| Tropical and subtropical vegetables | Fundamentals of food technology |
| Communication skills | Introductory microbiology |
| - | Water management in horticulture crops |
| SEMESTER III | SEMESTER IV |
| Temperate fruits | Spices |
| Ornamental horticulture | Commercial floriculture |
| Biochemistry | Plantation crops |
| Fundamentals of entomology | Orchard management |
| Principles of plant breeding | Breeding of fruits |
| Temperate vegetables | Mushroom culture |
| Tuber crops | Environmental science |
| - | Insect ecology |
| - | Soil science I |
| SEMESTER V | SEMESTER VI |
| Organic farming | Remote sensing |
| Introduction of major field crops | Entrepreneurship development |
| Introductory agroforestry | Seed production |
| Apiculture | Medicinal and aromatic plants |
| Post-harvest management | Processing of horticulture crops |
| Principles of plant biotechnology | Horticulture business management |
| Breeding and seed production | - |
B.Sc. in Horticulture: Career Prospects
Horticulture is a field that holds ample scope. Whether they want to be full-time or part-time horticulturist, whether they have your own piece of land or not, they can take up this line and make a decent living out of it. Some advances in horticultural technology, increases product demands, and a growing export industry are making this an extremely lucrative career. Opportunities are being created in fields such as research and journalism, in both the sectors public and private, and they also work within and outside of our borders.
Job opportunities are available for Graduates in Government as well as Private sector. Government sector jobs, and Officer level posts are available for these Graduates in State wise Forestry Departments, State wise Agriculture Departments, as well as Boards like Spice or Coir or Rubber boards etc. Private Sector job opportunities are available in areas such as Private Plantations, Ornamental plants and flowers businesses, Agricultural Products marketing firms, Agricultural Machinery and Equipment manufacturing firms, Food Production and Technology Industry etc.
Some of the top professional avenues open to such postgraduates are listed below with the corresponding salaries offered for the respective positions.
%20annual%20salary.png)
| JOB POSITION | JOB DESCRIPTION | AVERAGE ANNUAL SALARY IN INR |
|---|---|---|
| Horticulturist | Horticulturists apply their knowledge, and technologies used to grow intensively produced plants for human food and non-food uses and for personal or social needs. Their work involves plant propagation and cultivation with the aim of improving yields, diseases, plant growth, nutritional value, quality, and resistance to insects, and environmental stresses. They also work as gardeners, therapists, designers, growers, and technical advisors in the food and non-food sectors of horticulture. | INR 2,50,000 |
| Plantation manager | A plant manager oversees the operations of a manufacturing facility and develops strategies to increase production at minimal costs. Some employees start out as production workers, they gain experience and work their way up to plant manager status. | INR 7,40,000 |
| Horticulture specialist | Horticultural workers prepare seed beds, they transfer plants to containers, and move container plants around the work site, unload shipments of packaged soil and other gardening products. Specialists may also propagate new plants through grafting and other measures, and prune plants and trees. | INR 6,00,000 |
| Technical assistant | Technical assistants are found in every field, including education, science, healthcare, engineering, computer science, arts, and more. Some specific duties vary by industry, most technical assistants work in some type of administrative capacity to support other professionals in their field. Technical assistants manage data; they develop correspondence, prepare reports, or spread sheets, and file paperwork. | INR 2,23,000 |
Eligibility Criteria
Candidate must have passed 10+2 in science stream from recognized board.
| Year (2019 - 2020) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuition fees | ₹5500 | ₹5500 | ₹5500 | ₹5500 |
| Exam fees | ₹415 | ₹415 | ₹415 | ₹415 |
| other fee | ₹4558 | ₹1618 | ₹1903 | ₹1618 |
| Yearly Fees | ₹10,473 | ₹7,533 | ₹7,818 | ₹7,533 |
Course Finder
Search from 20K+ Courses and 35+ Streams
Popular Streams:
RVSKVV Latest News
RVSKVV Result 2022 (Released) @rvskvv.net: Check B.Sc, M.Sc & PhD Results



![Rajmata Vijayaraje Scindia Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya - [RVSKVV]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1415016954LOGO-RVSKVV.jpg?h=71.7&w=71.7&mode=stretch)





![Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya - [JNKVV]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/14890520462.jpg?h=111.44&w=263&mode=stretch)




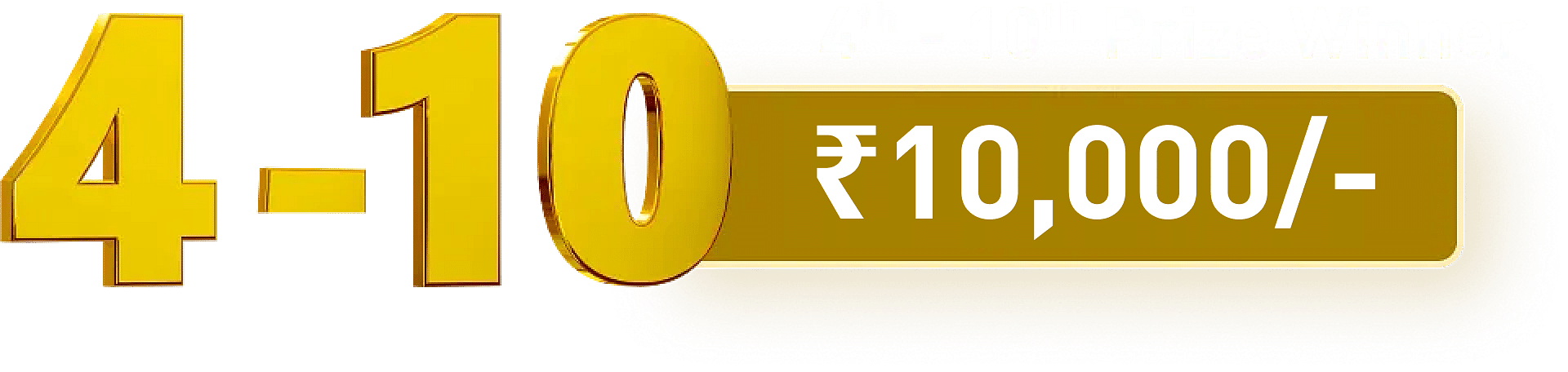


![Forest College and Research Institute - [FCRI]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1426239151logo.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![University of Agricultural Sciences - [UAS]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1460805769UniversityofAgriculturalSciencesDharwad.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)

![Agricultural College and Research Institute - [ACRI]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1467200135logo1.png?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Indian Institute of Pulses Research - [IIPR]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6642.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru College of Agriculture & Research Institute - [PAJANCOA & RI]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1486386291indexpajancoaemblem.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth - [PDKV]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1464602201Capture.JPG1.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)

![Central Institute for Arid Horticulture - [CIAH]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6530.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)

![Indian Institute of Rice Research - [IIRR]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1458278449loho.png?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![University of Agricultural and Horticultural Sciences - [UAHS]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1422531917logo.png?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)



Comments