RVSKVV M.Sc Horticulture: Fees 2025, Course Duration, Dates, Eligibility
Course Description
Master of Science in Horticulture Top Colleges, Syllabus, Scope and Salary
M.Sc. in Horticulture is a 2-year postgraduate program specialization in the agricultural field. The course is divided into 4 semesters, with each semester lasting a period of 6 months. Each semester contains a separate set of theoretical subjects and practical lab sessions.
Horticulture is the most dynamic and career-oriented sector of agriculture. It deals with:
- cultivation and primary processing of plants.
- management, consulting, activity organization.
- quality assurance, marketing and after-services.
- production and marketing of horticultural enterprises.
| Master of Science in Uttar Pradesh | Master of Science in Uttarakhand | Master of Science in Tamil Nadu | Master of Science in Maharashtra |
Qualified professionals of the course can work as:
- managers
- counsellors
- research scientists
- educators.
The program has been designed to build in eligible students:
- knowledge of horticultural and natural sciences.
- awareness of interdisciplinary aspects such as crop rotation and cultivation.
- relevant understanding of subjects like:
- genetics
- physiology
- ecology
- biometrics.
- advanced understanding of:
- fruits
- medicinal plants
- vegetables
- ornamental flowers
- grape and wine.
The course consists of components such as:
- theoretical lectures
- laboratory work
- farm practices
- field visits.
Specializations offered as part of the course include:
- Biotechnology
- Plant and Soil Biochemistry
- Crop Management
- Economics
- Plant Cultivation
- Research
- Genetics
- Crop Ecophysiology.
The average course fee in India ranges between INR 3,000 - 80,000 for the total duration. The average annual salary offered to successful postgraduates of the field lies between INR 5-7 lacs.
M.Sc. in: Course Highlights
Tabulated below are some of the major highlights of the course.
| Course Level | Postgraduate |
| Duration | 2 years |
| Examination Type | Semester System |
| Eligibility | Graduation from a recognized university |
| Admission Process | Direct admission to colleges. Entrance test in some cases. |
| Course Fee | INR 5,000 - 80,000 |
| Average Starting Salary | INR 5-7 lacs |
| Top Recruiting Fields/Areas | Private Plants, Agricultural Machinery and Equipment Manufacturing Firms, Fertilizer Production Companies, Marketing Firms, Ornamental and Medicinal Plants and Flowers Businesses, Food Production and Technology, Landscape Design and Interior Design firms, Private Colleges, Agriculture Department, Forest Department, Fertilizer Production Units, Plant Breeding, Turfgrass Management, Landscape Design and Urban Horticulture, among others. |
| Job Titles | Horticulturist, Floriculturist, Pomologist, Fruit Juice Companies, Garden/Orchard owner, Food Processing Plants, Scientist in research studies, and such. |
M.Sc. in Horticulture: What is it About?
Horticulture is defined as the art, science and technology of growing and cultivating plants. These plants may be:
- medicinal or ornamental
- fruits
- vegetables
- nuts
- seeds
- seaweeds
- herbs
- sprouts
- mushrooms
- flowers
- non-food crops such as grass.
Students enrolled to the course are imparted advanced lessons in:
- Plant Breeding
- Biochemistry
- Yield-improvement
- Seed Technology
- Plant Cultivation
- Plant Physiology
- fundamentals of Physical Science, Biology and Technology.
M.Sc. in Horticulture: Who should opt?
Ideal candidates for the course would possess:
- interest in gardening, agriculture and similar studies.
- good leadership and team-management skills.
- affinity for science subjects like:
- Plant Physiology
- Horticultural Biology
- Molecular Plant Science
- Crop Development.
Top Institutes offering M.Sc. in Horticulture
Listed below are some of the top institutes offering the course in the country with the corresponding locations and fees charged by each.
| Name of Institute | City | Average Fees per annum in INR |
| Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth - [PDKV] | Akola | 9,086 |
| Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University - [BBAU] | Lucknow | 50,000 |
| BFIT Group of Institutions | Dehradun | 49,500 |
| Central Agricultural University - [CAU] | Imphal | 74,000 |
| Tamil Nadu Agricultural University | Coimbatore | 16,700 |
| University of Horticultural Sciences | Bagalkot | 21,400 |
| Dr. YSR Horticultural University | Tadepalligudem | 32,100 |
| Uttaranchal (P.G.) College of Biomedical Sciences & Hospital | Dehradun | 30,000 |
| Dr. YS Parmar University of Horticulture and Forestry - [YSPUHF] | Solan | 40,000 |
| Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University | Samastipur | 15,000 |
Eligibility for M.Sc. in Horticulture
Candidates aspiring for admission to the course are required to fulfill the following minimum eligibility criteria.
- Graduation completed from a recognized university.
- Preferably, graduation needs to have been completed in a relevant discipline, such as:
- B.Sc. Horticulture
- B. Sc. in Applied Sciences
- B.Sc. Agriculture
- Agricultural Engineering
- Agricultural Information Technology.
- A minimum aggregate score of 50% (45% for SC/ST/OBC candidates) at the level of graduation.
- Candidates appearing for their final graduation-level examination are also eligible to apply for the course on provisional basis.
| Master of Science in Rajasthan | Master of Science in Madhya Pradesh | Master of Science in Andhra Pradesh | Master of Science in Bihar |
M.Sc. in Horticulture: Admission Process
Most institutes offering the course in India admit students based on their performance in a relevant entrance test, followed by a subsequent round of counselling.The round of counselling consists of two additional rounds of group discussion and personal interview, wherein the candidate’s general aptitude for the course is examined.
Some institutes conduct their own entrance tests for offering admission. Admission process generally varies across colleges. A few institutes also provide direct admission based on the candidate’s score at the level of graduation.
M.Sc. in Horticulture: Syllabus and Course Description
A semester-wise breakup of the course’s syllabus is tabulated below
Semester 1 |
Semester 2 |
| Plant Biochemistry | Plant Breeding |
| Plant Microbiology | Seed Technology |
| Biotechnology | Agricultural Meteorology |
| Plant Physiology | Agronomy |
| Molecular Biology | Soil Science and Engineering |
| Plant Genetics | Agricultural Chemistry |
Semester 3 |
Semester 4 |
| Fertilizer Technology | Floriculture |
| Entomology | Plantation Management |
| Plant Pathology | Landscape Architecture |
| Agricultural Economics | Medicinal and Aromatic Plants |
| Agricultural Extension | Field Study |
| Post-Harvest Technology | Thesis |
M.Sc. in Horticulture: Career Prospects
Popular areas of employment for such postgraduates include:
- Agriculture Department
- Forest Department
- Fertilizer production units
- Academia
- Private Plants
- Agricultural Machinery and equipment manufacturing firms
- Fertilizer production companies
- Marketing firms
- Ornamental and Medicinal plants and flowers businesses
- Food Production and Technology
- Productions and Sales
- Public Gardens
- Marketing, Research and Development Sector
- Landscape Design, Agriculture
- Landscape Design and Interior Design firms
- Private Colleges, etc.
Such professionals are hired in capacities such as:
- Horticulturist
- Floriculturist
- Pomologist
- Scientist in research studies.
Some of the popular professional avenues open to successful postgraduates of the course are listed below with the corresponding salaries offered for the respective positions.
![Master of Science [M.Sc.] in Horticulture annual salary](https://images.collegedunia.com/public/image/Master%20of%20Science%20%5BM_Sc_%5D%20in%20Horticulture%20annual%20salary.png)
| Job Position | Job Description | Average Annual Salary in INR |
| Horticulturist | Horticulturists work the production and cultivation of plants. They are work to improve plant growth, quality, nutritional value, yield, and resistance to insects, diseases. Also, they are involved in research work, and perform research on plants to produce new breeds and yields. Their job starts as gardeners and designers. They grow and act as therapists, designers, and often act as technical advisors for the organization they work in. | 4-7 lacs |
| Floriculturists | Floriculture is a part of horticulture, and is a process of cultivation of fragrant flowers used as a raw material in the making of perfumes and cosmetics in the pharmaceutical industry. A Floriculturist cultivates flowering and ornamental plants on a large scale. They take care of flower gardens, work in floral industries, and for export. They also develop new plant varieties. | 3-6 lacs |
| Pomologist | A Pomologist is responsible for ensuring healthy growth and breeding of fruits and nuts, and also the trees and bushes on which the fruits grow. | 4-6 lacs |
| Soil Scientist | Soil Scientists examine different soils from a variety of terrains and geographical locations. Their job is to study the soil's physical composition and chemical properties. Soil Scientists assess, evaluate, and record the impact of the quality of soil on agriculture. | 4-6 lacs |
| Seed Analyst | Seed Analysts are responsible for testing and analyzing seeds for purity, type, viability, and germination rate. They follow the standards set by the government or private organization they work for. They shuffle between lab and field settings. They may also travel to explore and produce hybrid seeds. | 3-6 lacs |
Eligibility Criteria
Candidate must possess graduation degree B.Sc in relevant field with 60% from this university or any other recognized university.
Admission Guidelines
- Selection of the candidate to the B.Sc course is done on the basis of entrance test being conducted by Professional Examination Board, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh (VYAPAM, Bhopal). Candidates selected by ICAR entry test shall be admitted over and above the prescribed seats from time to time
- Selection of candidate to M.Sc and Ph.D programme is done on the basis of merit in the qualifying examination. However, preference will be given to the students of the V.V.
| Years (2018 - 2019) | year 1 | year 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semester | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Tuition fees | ₹9380 | ₹9380 | ₹9380 | ₹9380 |
| other fee | ₹5645 | ₹3215 | ₹3215 | ₹3215 |
| Semester Wise Fees | ₹15025 | ₹12595 | ₹12595 | ₹12595 |
| Yearly Fees | ₹27,620 | ₹25,190 | ||
Course Finder
Search from 20K+ Courses and 35+ Streams
Popular Streams:
RVSKVV Latest News
RVSKVV Result 2022 (Released) @rvskvv.net: Check B.Sc, M.Sc & PhD Results



![Rajmata Vijayaraje Scindia Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya - [RVSKVV]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1415016954LOGO-RVSKVV.jpg?h=71.7&w=71.7&mode=stretch)





![Jawaharlal Nehru Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya - [JNKVV]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/appImage/14890520462.jpg?h=111.44&w=263&mode=stretch)




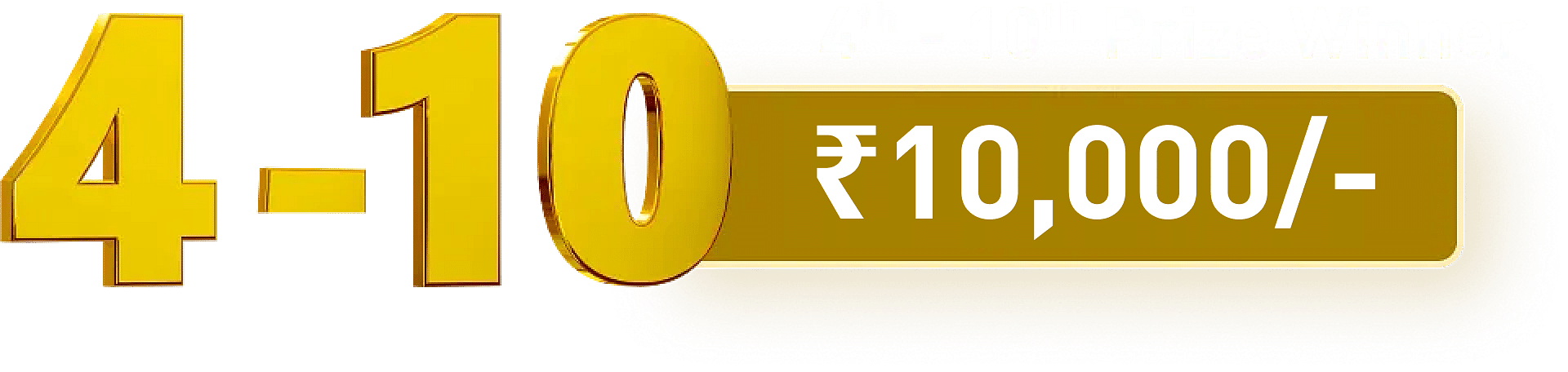

![Forest College and Research Institute - [FCRI]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1426239151logo.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)

![Indian Institute of Rice Research - [IIRR]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1458278449loho.png?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Central Institute for Arid Horticulture - [CIAH]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6530.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![University of Agricultural and Horticultural Sciences - [UAHS]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1422531917logo.png?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Indian Institute of Pulses Research - [IIPR]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/col6642.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)

![Agricultural College and Research Institute - [ACRI]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1467200135logo1.png?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth - [PDKV]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1464602201Capture.JPG1.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)


![University of Agricultural Sciences - [UAS]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1460805769UniversityofAgriculturalSciencesDharwad.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)
![Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru College of Agriculture & Research Institute - [PAJANCOA & RI]](https://image-static.collegedunia.com/public/college_data/images/logos/1486386291indexpajancoaemblem.jpg?h=72&w=72&mode=stretch)



Comments